👉🏻 타입스크립트는 자바스크립트 + 타입입니다.
TypeScript is JavaScript + types.
👉🏻 자바스크립트는 자동으로 타입을 추론 할 수 있습니다. 하지만 기능이 부족할 경우 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.
JavaScript can automatically infer types, but if the functionality is lacking, errors can occur.
👉🏻 타입을 사용함으로 자바스크립트의 자동추론을 보완 할 수 있습니다.
Using types can complement JavaScript’s automatic inference.
👉🏻 타입스크립에서 타입을 사용하는 경우는 변수, 함수 파라미터/반환값, state, props, 객체/배열, 제네릭, 타입 별칭/인터페이스 등 거의 모든 값이 들어가는 곳에 타입을 정의할 수 있습니다.
When using types in TypeScript, you can define types for almost any value, including variables, function parameters/return values, state, props, objects/arrays, generics, type aliases/interfaces, etc.
👉🏻 아래의 코드는 타입의 사용빈도가 높은 부분에 대한 예제입니다.
The code below is an example of a frequently used part of the type.
👉🏻 프로젝트 생성 / Create project
% npm create vite@latest ReactExample4 --template react-ts
% cd ReactExample4
% npm install
# 서버 실행(실행 테스트) / Running the server (running test)
# Run the server (run test)
% npm run dev👉🏻 프로젝트 구조 / Project structure
src/
├─ types.tsx
├─ components/
│ └─ UserCard.tsx
├─ App.tsx
├─ main.tsx👉🏻1. 전역 타입 정의 (src/types.ts)
Global type definitions (src/types.ts)
// 여러 컴포넌트에서 공유할 타입 정의
export type Todo = {
id: number;
text: string;
completed: boolean;
};👉🏻2. Props 타입 지정 (src/components/UserCard.tsx)
Specifying Prop types (src/components/UserCard.tsx)
import React from "react";
type UserCardProps = {
name: string;
age?: number; // 선택적 props / optional props
};
const UserCard: React.FC<UserCardProps> = ({ name, age }) => {
return (
<div style={{ border: "1px solid gray", padding: "10px", margin: "5px" }}>
<h2>{name}</h2>
{age && <p>Age: {age}</p>}
</div>
);
};
export default UserCard;
⭐️ React.FC<UserCardProps>
✔️ React.FC를 사용하면 children porps가 자동 포함됩니다.(타입에 children을 정의하지 않아도 됩니다.)
React.FC automatically includes children types (you don’t need to define children in your types).
✔️ 필요한 경우 꺼내서 사용 할 수 있고 사용하지 않을 수도 있습니다.
You can take it out and use it if you need to, or you can leave it out if you don’t.
const UserCard: React.FC<UserCardProps> = ({ name, age, children }) => {
return (
<div style={{ border: "1px solid gray", padding: "10px", margin: "5px" }}>
<h2>{name}</h2>
{age && <p>Age: {age}</p>}
<div>{children}</div> {/* 여기서 children 출력 */}
</div>
);
};✔️ children을 자동으로 포함하지 않을 경우 아래처럼 사용 할 수도 있습니다.
If you don’t want to automatically include children, you can use it like this:
type UserCardProps = {
name: string;
age?: number;
};
function UserCard({ name, age }: UserCardProps) {
return (
<div>
<h2>{name}</h2>
{age && <p>Age: {age}</p>}
</div>
);
}👉🏻3. State 타입 지정 + 함수 타입 지정 (src/App.tsx)
State type specification + function type specification (src/App.tsx)
import React, { useState } from "react";
import UserCard from "./components/UserCard";
import type { Todo } from "./types";
// 함수 타입 지정: string을 받아 string을 반환
// Function type specification: takes a string and returns a string
function greet(name: string): string {
return `Hello, ${name}!`;
}
function App() {
// State 타입 지정
// Specify State type
const [todos, setTodos] = useState<Todo[]>([
{ id: 1, text: "Learn Vite", completed: false },
{ id: 2, text: "Practice TypeScript", completed: true },
]);
// 만약 toggleTodo(3)을 호출하면, id가 3인 todo를 찾아서 completed 값을 반전시킵니다.
// If you call toggleTodo(3), it will find the todo with id 3 and invert its completed value.
const toggleTodo = (id: number) => {
setTodos((prev) =>
prev.map((todo) =>
todo.id === id ? { ...todo, completed: !todo.completed } : todo
)
);
};
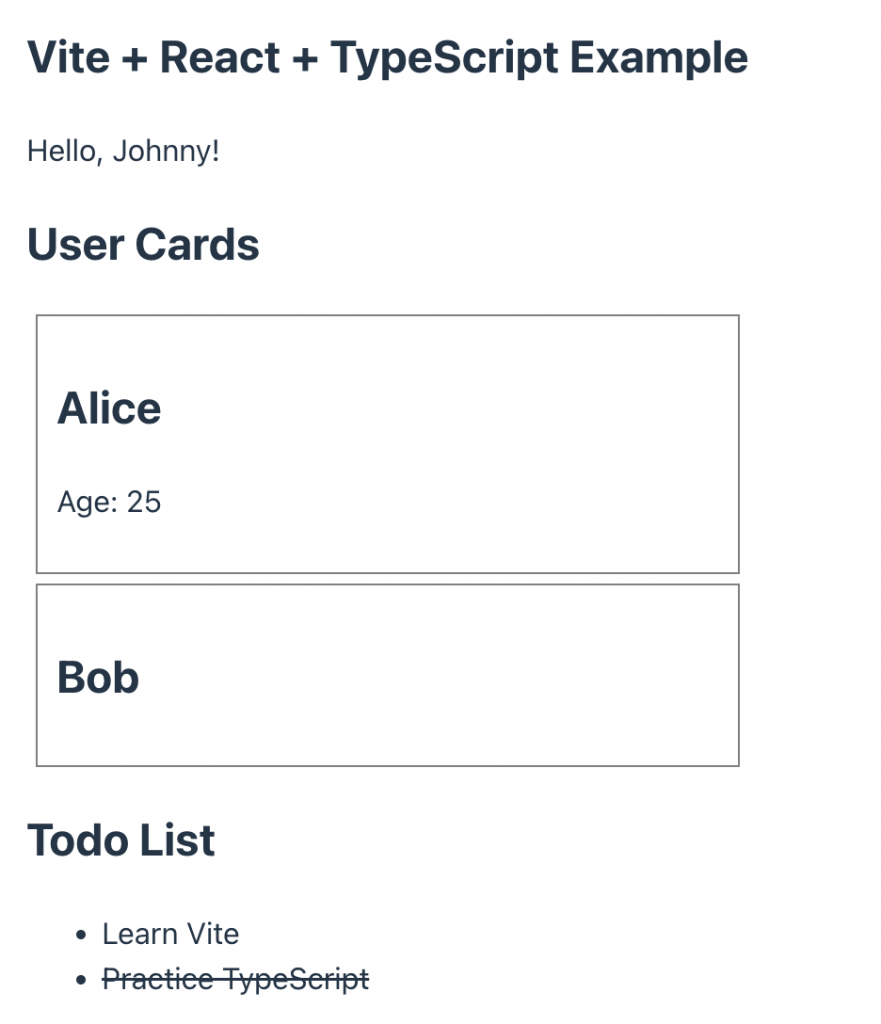
return (
<div style={{ padding: "20px" }}>
<h3>Vite + React + TypeScript Example</h3>
<p>{greet("Johnny")}</p>
<h2>User Cards</h2>
<UserCard name="Alice" age={25} />
<UserCard name="Bob" />
<h2>Todo List</h2>
<ul>
{todos.map((todo) => (
<li
key={todo.id}
style={{
textDecoration: todo.completed ? "line-through" : "none",
cursor: "pointer",
}}
onClick={() => toggleTodo(todo.id)}
>
{todo.text}
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
⭐️ 기존 상태반전 / Inversion of existing state
✔️prev.map(…)
— prev는 이전 todos 배열입니다.
prev is the previous todos array.
— map을 사용해서 배열을 순회하면서, id가 일치하는 todo만 completed 값을 반전시킵니다.
Using map, we iterate through the array and invert the completed value only for todos with matching id.
— { ...todo, completed: !todo.completed } 이 구문은 기존 todo 객체를 복사한 뒤, completed 속성만 반전시켜서 새로운 객체를 반환하는 방식입니다.
{ …todo, completed: !todo.completed } This syntax copies the existing todo object and returns a new object with only the completed property reversed.
const toggleTodo = (id: number) => {
setTodos((prev) =>
prev.map((todo) =>
todo.id === id ? { ...todo, completed: !todo.completed } : todo
)
);
};👉🏻4. 진입 파일 (src/main.tsx)
Entry file (src/main.tsx)
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import App from "./App";
import "./index.css";
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root")!).render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
👉🏻5.스크린 샷 / ScreenShot